Does CBD Oil Work for Migraine?

Migraine is a neurological condition that affects many people across the world. It is estimated to rank third in the global list of most common diseases after tension headache and dental caries. The estimated prevalence worldwide for migraine, according to ‘The Migraine Trust,’ is 14.7%, which translates to about one in seven people. About 2% of the world’s population suffers from chronic migraine.
According to historical evidence, medical cannabis has been used to prevent and treat headache disorders, including migraine. Being safe and non-psychoactive, CBD has the potential to emerge as a mainstream therapy for migraine.
Prevalence
Globally, migraine is ranked seventh in the list of most disabling diseases, while being the leading disability cause among all neurological conditions. The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies it as a disabling illness that is comparable to other neurological disabling conditions such as quadriplegia, dementia, and psychosis.
According to estimates from WHO, the worldwide migraine prevalence is 10%, while lifetime prevalence is 14%. The high prevalence is noted in North America, Central and South America, Asia, Europe, and Africa. Every day, about 3000 migraine attacks occur per million people across the world.
Migraine is believed to be more widespread than asthma, diabetes, and epilepsy combined. The female to male gender prevalence ratio of migraine is 3:1, suggesting the condition could be hormone-driven. Migraine sufferers experience at least one migraine attack in a month, with more than 50% of these experiencing severe functional impairment during these attacks.
While this condition often starts during puberty, it mostly affects people in the age group of 35 to 45 years. However, younger children can also suffer from migraine. While an estimated 4% of girls and boys get migraine in pre-pubertal age, among older adults, the condition predominantly is seen in women.
In the UK, 25 million days are lost at school or work every year due to migraine. About 18% of the population in the US suffers from migraine.
What is migraine?
Migraine is a recurring, neurovascular, disabling headache disorder. While it strikes a few times in a year in childhood, it progresses to cause more frequent attacks in adulthood for sufferers, particularly in females.
Attacks are preceded by prodromes or warning signs, while some people experience ‘migraine aura,’ which are focal neurological symptoms that are transient.
In some instances, there are no warning signs for the headache. The prodromal phase that many migraine sufferers experience can include a range of symptoms, such as depression, fatigue, food cravings, irritability, neck stiffness, constipation, increased yawning, and heightened sensitivity to sound, smell, or light.
The aura phase comprises many neurological symptoms that occur just before the headache starts and can last throughout the attack. Migraine aura symptoms can develop gradually or at times suddenly where the sufferer experiences scintillating/zig-zag lights, blind spots that can block vision, numbness and tingling of hands, face, limbs, or on one side of the body, paresthesia, tremors, and unilateral muscle weakness. There is also difficulty with speech.
This is followed by an intense, throbbing headache with increased intracranial pressure. The headaches are typically accompanied by nausea and vomiting, apart from an abnormal, heightened sensitivity to smell, noise, and light. Some migraine sufferers also experience muscle tenderness and abnormal skin sensitivity known as allodynia.
The headache can last for a few hours to many days, and its progression is marked by multiple symptoms involving different neuronal systems:
- Autonomic symptoms include:
- nasal congestion, nausea, vomiting, frequent urination, yawning, diarrhea, fatigue.
- Affective symptoms include:
- irritability and depression.
- Cognitive symptoms include:
- transient amnesia, attention deficit, speech difficulty or problem finding words, difficulty in movement /finding one’s way even in familiar surroundings.
- Sensory symptoms include:
- Photophobia (aversion to light), phonophobia (fear or aversion to sound), osmophobia (aversion to smell), sensitivity to touch, and muscle tenderness.
The progression of symptoms from the prodromal/aura stage to the headache stage indicates the involvement of multiple neuronal systems.
What causes migraine?
Migraine typically has genetic and familial causes with one or multiple family members also having a history of migraine. While hormonal fluctuations in women are believed to trigger attacks, the other triggers include:
- Tyramine-rich foods, such as yeast extract, cured meats, smoked fish, and cheeses, including camembert, cheddar, stilton
- Caffeine
- Chocolate
- Alcohol
- Skipping meals/fasting
- Lack of sleep
- Dehydration
- Bright lights/flickering screens
- Loud noises
- Strong smells
- Temperature/weather changes
- Anxiety, stress, depression, or shock
- Bright lights, including harsh sunlight
- Smoking (or smoky rooms)
- Loud noises/strong smells
- Low blood sugar
- Strenuous physical activity/exercise
The background of CBD
Cannabis has been used by humans for centuries, with the first documented use being in the 3rd millennium BC. The archaeological evidence that is available suggests the possibility that Cannabis was used even earlier. After the psychoactive, addictive effect of cannabis was discovered, restrictions were imposed on the use of cannabis in the 14th century, and by the 20th century, countries across the world banned cannabis for recreational use.
With scientists discovering many other facts in the 1980s related to the role of the endocannabinoid system, cannabinoid receptors, and the roles they play in physiological functions, a collective understanding of medical cannabis was enhanced. The beginning of the 21st century has witnessed changes in approaches of governments to cannabis. It has been legalized in some countries while others are exploring the potential medicinal properties of cannabis extracts, mainly, cannabidiol (CBD). This component found in cannabis plants has attracted the attention of researchers and people across the world for its therapeutic potential.
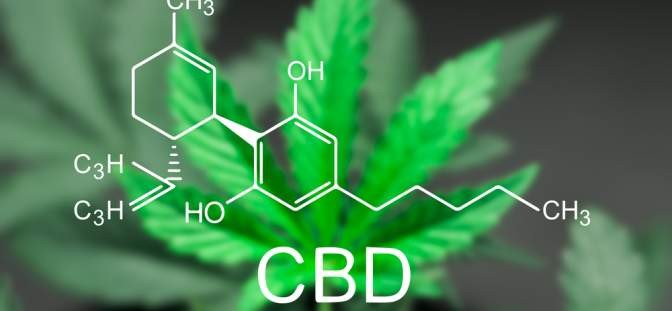
Cannabidiol or CBD belongs to a group of compounds called cannabinoids that are present exclusively in Cannabis Sativa plants. The psychoactive compound THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is also a cannabinoid, while CBD has no psychoactive effect. More than 500 different chemicals are known to be present in Cannabis Sativa plants. Some varieties of Cannabis plants are grown for the purpose of developing medicinal products, and these varieties are rich in CBD while having little to no THC. Marijuana plants, as per the U.S. FDA (Food and Drug Administration), classification are those varieties of Cannabis Sativa plants that contain more than 0.3% of THC.
The entire cannabis plant is used to extract CBD, which is typically produced in powder form using traditional solvent extraction or high-tech CO2 extraction methods. The CBD extracted are purified and incorporated as an isolate or a concentrate in topical products such as facial cream, eye serum, sleeping mask, body oil, or pain relief spray. CBD is mixed with essential/carrier oils with established therapeutic properties such as hemp, coconut, almond, or olive oils.
While anywhere between 61 to 66 chemicals out of the 500 compounds found in cannabis plants are categorized as cannabinoids, 18 chemical groups present in CBD, such as fatty acids, amino acids, terpenes, nitrogenous compounds, and hydrocarbons, impart therapeutic action.
Cannabis plants are flowering plants that have, for years, been cultivated for recreational, medicinal, industrial, and spiritual purposes. Extractions of the cannabis plant in spray, powder, or oral versions have been studied for their anti-inflammatory, anti-spasmodic, analgesic (pain relief), muscle relaxant, and anti-anxiety effects.
Can CBD oil help control migraine?
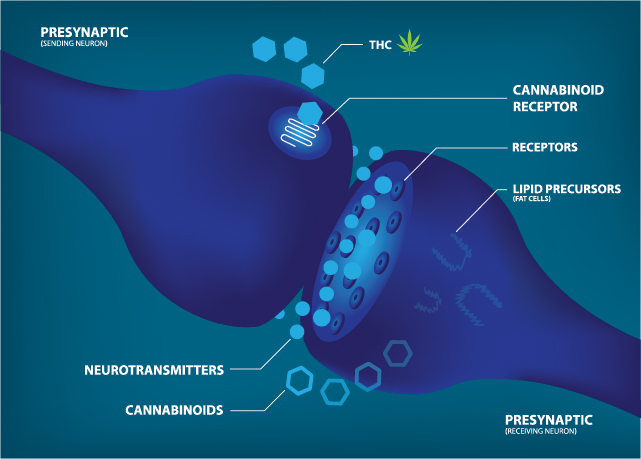
CBD-integrated topical products such as body oil, Pain Relief Spray indirectly activate endocannabinoid receptors in the brain. A vast number of CB1 receptors are located in the brain, and by indirectly interacting with them, CBD oil helps control pain while relieving joint stiffness and muscle tenderness associated with migraine.
Two systematic reviews were conducted to evaluate the efficacy of CBD in providing relief from chronic pain of non-cancerous origin that includes rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia, neuropathic pain, and other conditions. Researchers reviewed 29 trials on CBD and found that CBD was effective in providing pain relief in 22 studies.
As both THC and CBD belong to the same group of compounds (cannabinoids), many of their actions are similar. THC is known to bind to cannabinoid receptors to bring about pain relief. Researchers, in a 2017 study, found that when CBD and THC were both administered, migraine sufferers experienced reduced frequency and intensity of migraine attacks. The study included two phases where a combination of CBD and THC were given. The first phase of the study involved the administration of two combinations where one had 9% CBD and no THC, while the second had 19% THC. A 55% reduction in pain was observed when the dosages of THC and CBD were increased optimally to 200 milligrams.
The second phase involved a comparison of cannabinoid active ingredients (THC and CBD) with the standard pharmacological therapy for migraine, amitriptyline. Researchers observed that the combination of CBD and THC was successful in providing relief from pain as compared to amitriptyline. It was also observed that migraine attack frequency reduced by as much as 40% with CBD and THC combination.
A 2016 interventional study sought to evaluate the efficacy of medical Cannabis on migraine by measuring the frequency of migraine headaches in a month while taking CBD. Researchers found that the frequency of migraine headaches decreased to 4.6 headaches in a month as compared to the previous 10.4 after using medical Cannabis. Close to 40% of patients reported positive effects where a majority stated CBD helped prevent migraine headaches while many reported a decreased frequency of attacks.
In another older study, medical cannabis offered superior relief to women suffering from migraine as compared to standard treatments that include ergots, opiates, and beta-blockers.
Numerous case reports suggest medical cannabis successfully provided relief from migraine while years of standard pharmacological treatments had failed. In other cases, cannabis effectively controlled the headache in the prodromal phase.
Various theories have been proposed by researchers to explain how medical cannabis or CBD exerts a positive influence on migraine headaches. It has been recognized that the homeostatic balance and physiological functions in the human body are influenced by the endocannabinoid system. This system includes two cannabinoid receptors called CB1 and CB2, as well as endocannabinoids (naturally occurring neurotransmitters in the human body that bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors).
Scientists propose that endocannabinoid deficiency through a complex pathway leads to neurogenic inflammation, aura, heightened sensitivity to sensory stimulations, and pain. Endocannabinoid deficiency can also suppress the expression of cannabinoid receptors, with the cumulative effect being sensory, vascular, and motor symptoms of migraine.
The Endocannabinoid system’s role concerning homeostatic upkeep underscores its importance in the maintenance of overall health. Disruptions in endocannabinoid production or functionality are connected to multiple mental state disturbances, specifically migraine. Migraine shares many symptoms with other chronic pain conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Deficiency of endocannabinoids has been linked to chronic pain in many such conditions.
Another study in animal models demonstrated that insufficient endocannabinoids cause inflammation. Lowered endocannabinoid function is found in migraine that causes reduced expression of CB1 and CB2 receptors that forms the basis for external supplementation of endocannabinoids.
The proposed mechanism of CBD relates to the activation of cannabinoid receptors and inhibition of endocannabinoid deficiency. Scientists proposed that variations in genes that code for CB1 receptors lead to reduced production of CB1 receptors that promote migraine attacks. Cupini et al propose that a possible migraine cause is endocannabinoid deficiency. Other studies show levels of endocannabinoids are decreased in the platelets of migraine sufferers.
These, and many other findings, suggest CBD-integrated pain relief spray, pain relief roll-on, and CBD body oil can be effective therapeutic agents for treating migraine.
Quality is key in selecting the right CBD product for migraine
Migraine is a chronic condition that recurs periodically. While you must consult your doctor before using CBD products, it is also important to know how to select the right CBD topical pain relief spray or CBD oil. There are many CBD-integrated topical products, such as pain relief sprays, pain relief CBD cream, pain relief roll-on, extra-strength pain relief CBD creams and gels.
Read the label of the CBD oil-infused product thoroughly and note the amount of CBD typically mentioned in milligrams per unit/dose. Check the quality policy and credentials of the team developing the CBD products before purchasing CBD oil for migraine.
More articles: