The Case for CBD Oil as a Treatment for Venous Insufficiency & DVT
CBD or cannabidiol has gained the attention of researchers and consumers worldwide due to its wide-ranging therapeutic properties. CBD-integrated beauty products, such as facial cream, eye serum, and so on, are growing in popularity owing to their natural anti-aging effects.
A large number of in vivo and in vitro studies indicate that CBD oil can be a safe and viable alternative to medications in treating vascular disorders such as deep vein thrombosis and chronic venous insufficiency.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis or DVT
External injuries or falls can, at times, lead to open wounds and bleeding. Without certain mechanisms that allow the formation of blood clots, we could probably bleed to death. These blood clots are essential and beneficial in terms of protecting the body against cuts, wounds, or injury, and preventing excessive bleeding. The clots normally dissolve on their own.
However, these blood clots can also, at times, cause a serious threat to life. Some blood clots in the veins that do not naturally dissolve can lead to severe problems. One such chronic problem is DVT or Deep Vein Thrombosis. DVT is the result of a blood clot within a deep vein that, when not treated, can be life-threatening.
Blood clots formed in the artery or veins are called thrombosis. When the thrombosis develops within the deep vein, commonly in the lower leg or thigh, the condition is called deep vein thrombosis.
Recent estimates show that deep vein thrombosis accounts for about one out of five deaths globally.
Additionally, DVT can contribute to other multiple permanent health issues.
While DVT can cause swelling and pain in affected areas (usually leg or thigh), many people with DVT may not experience any symptoms.
When untreated, DVT can lead to a serious condition known as pulmonary embolism. This is a condition where a part of the blood clot in the deep vein in the leg or thigh breaks up and travels through the bloodstream to reach the lungs. The clot then blocks the blood supply to the lungs and can be fatal.
Many risk factors are linked to DVT, such as
- Injury to veins, surgery, muscle injury
- Poor blood flow due to immobility caused by illness or surgery
- Prolonged periods of sitting, particularly by crossing legs, such as in long-haul flights
- Family history
- Heart disease history
- Other clotting disorders
- Certain medications given to treat excess bleeding
What is venous insufficiency?
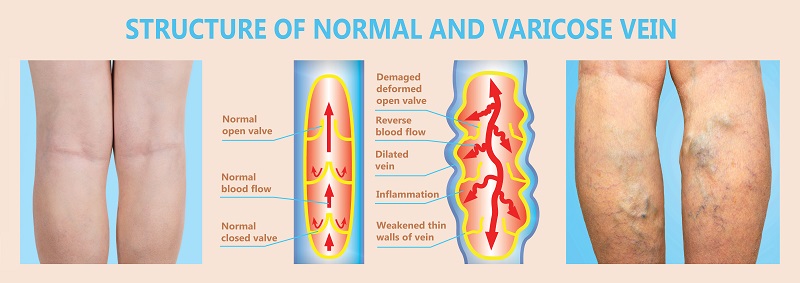
Venous insufficiency, also called CVI or Chronic venous insufficiency, is one of the most common causes behind swelling and pain in the legs. The condition is linked to varicose veins. CVI is caused by improperly functioning valves in the veins that impact blood circulation. Valves in leg veins normally function to ensure blood flows to the heart. These valves have a one-way function, which means the blood cannot flow back to the legs. In chronic venous insufficiency, the valves do not function the way they should, leading to pooling of blood in the legs, causing CVI.
Close to 20% of the adult population is believed to suffer from CVI. Damage to valves or blockage in veins can both cause CVI. As per another estimate, 150,000 new patients approximately are diagnosed each year with chronic venous insufficiency.
Such damage or blockage can also occur due to DVT or deep vein thrombosis, where blood clots form in the legs.
CVI causes varicose veins over time marked by discoloration and swelling of the legs, development of ulcers around ankles, and itching.
Both CVI and DVT impair the quality of life and are responsible for the reduction in the number of working days and loss of productivity.
Surgery is often the treatment for varicose veins where the troublesome veins are removed by stripping. Studies show that even patients who have varicose vein removal surgery experience a relapse where there is not only clinical recurrence, but the disease can progress to previously unaffected leg veins. The other treatments used are ablation using lasers, radiofrequency energy or sclerotherapy, as well as drug therapy.
Cannabidiol’s role in treating venous insufficiency and deep vein thrombosis
Cannabidiol or CBD has been found to have beneficial effects with respect to treating many chronic conditions such as cancer, ulcerative colitis, Huntington’s disease, diabetes, fibromyalgia, epilepsy, and migraine.
Both deep vein thrombosis and vascular insufficiency are considered to be conditions that pertain to the cardiovascular system.
Accumulating evidence indicates CBD-integrated products are also beneficial to the cardiovascular system. CBD exerts a direct action on arteries, resulting in time-dependent and immediate relaxation of arteries (vasorelaxation). In vitro studies in animal models show that CBD boosts the vasorelaxant effect in arteries.
CBD is also known to have a protective effect on vascular damage that is typically caused by high glucose load and inflammation in animal models associated with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes. These actions are attributed to the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of CBD.
CBD treatment prevents inflammation and damage to the heart that is linked to uncontrolled diabetes. CBD, in other experimental models, has been known to reduce the size of damage to the heart that can occur as a result of a stroke while also enhancing blood flow.
In blood, CBD has an influence on the survival of immune cells, including white blood cells, as well as clotting mechanisms related to platelet aggregation. This preclinical data, taken together, suggest that CBD can play a supportive role in treating conditions associated with heart, as well as peripheral vasculature (veins and arteries).
What is CBD?
CBD or cannabidiol is a non-psychoactive substance derived from the Cannabis Sativa plant. The Cannabis plant contains a group of compounds called cannabinoids that are exclusive to the plant.
About four hundred or more of compounds have been identified in Cannabis Sativa plant, out of which between 66 and 100 compounds are termed as “cannabinoids.” One of the compounds that have received attention is the delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol or THC, which is the active ingredient in marijuana responsible for the psychoactive effect.
Other cannabinoids in the Cannabis Sativa plant include:
- Cannabidiols or CBD
- Cannabichromenes or CBC
- Cannabigerol or CBG
- Cannabinol or CBN
- Cannabinodiol or CBDL
- Other cannabinoids such as CBE (cannabielsoin), CBT (cannabitriol), CBL (cannabicyclol), among others.
Although structurally similar to THC and CBN, cannabidiols are known for their therapeutic properties and can also inhibit the psychoactive effect of THC.
CBD is closely related to naturally occurring compounds in the human body known as endocannabinoids. These endocannabinoids are neurotransmitters and are involved in relaying signals to the brain cells by binding to receptors called CB1 and CB2 (cannabinoid receptors).
Endocannabinoids, along with the cannabinoid receptors, constitute the Endocannabinoid system (ECS) that plays a key role in maintaining the balance of physiological and psychological functions.
Lack of cannabinoid receptors or insufficient endocannabinoids is linked to many disease conditions, including chronic pain, allergies, migraine, heart disease, and other conditions.
The endocannabinoid system or ECS has a major role to play in the cardiovascular system, specifically in conditions that impact the health of blood vessels (vasculature). Researchers have observed that while ECS functions are disrupted in disease conditions, dysregulation of ECS itself may be the contributing factor for diseases. In vivo and in vitro studies indicate ECS dysfunction leads to the development of disease conditions related to the arteries and blood vessels, indicating the therapeutic potential of endocannabinoids.
CBD is a synthetic analog of natural endocannabinoids and has been shown to have important effects on the health of the cardiovascular system, as well as the complex mechanisms that affect the vasculature (blood vessels), such as in DVT and chronic venous insufficiency. The therapeutic potential of ECS system modulation has, therefore, been suggested to treat various disorders that relate to the cardiovascular system, including blood vessel and blood circulation-related disorders.
Vascular effects of CBD
The integrity of blood vessels (vascular tone) is influenced by certain cells that release vasoactive substances such as nitric oxide, substance P, prostacyclin, and others. These compounds are responsible for the relaxation of blood vessels. Damage to blood vessels occurs as a result of inflammation and accelerated platelet adhesion on the surface of blood vessels in atherosclerosis. Inflammation further triggers the production of pro-inflammatory substances, including chemokine receptors and chemokines. This leads to chronic inflammation of blood vessels, which is linked to deep vein thrombosis and venous insufficiency.
Researchers have studied CBD’s vascular effects in multiple models. Wide-ranging in vitro and in vivo studies indicate endocannabinoids (indigenous, natural cannabinoids) and phytocannabinoids (CBD) cause vasorelaxation.
Additionally, many studies also demonstrate that endocannabinoids help in healing cardiovascular injury and damage, apart from preventing the scarring of arteries (atherosclerosis).
Deep vein thrombosis is commonly treated using blood thinners or anticoagulants. These drugs are either in the form of pills or injections and decrease the ability of blood to form clots.
Past studies indicate that CBD has anticoagulant properties. A 2007 study sought to explore the anticoagulant effects of CBD in animal models. The study published in Phytomedicine involved exploring the anticoagulant effect of organic cannabis extract on obese mice. The extract contained CBD as well as other cannabinoids. Researchers found that cannabinoids significantly inhibited clot formation and concluded that cannabinoids had immense potential in treating blood clot-related conditions such as DVT.
One of the most common blood thinners prescribed to treat deep vein thrombosis is Warfarin.
A type of liver enzyme called Cytochrome P450 or CYP450 plays a key role in metabolizing warfarin and enabling its action on clotting mechanisms. A 2017 study showed that CBD is also metabolized in the same way through the CYP450 enzyme. The pathway of metabolism and action were found to be similar for both warfarin and CBD.
Cannabinoids raise the level of natural blood thinners in the body, although more studies are needed to confirm this.
Enhanced venous pressure and inflammation are the typical characteristics of venous insufficiency. Many mechanisms are believed to contribute to blood vessel damage in venous insufficiency.
Oxidative stress and inflammation are also implicated in the development of varicose veins, which is a contributory factor for chronic venous insufficiency. Oxidative stress is a condition where the number of natural antioxidants in the body are lesser than the harmful free radicals. Free radicals are byproducts of metabolic processes and are generated in the pathways where energy is produced in the cells. These radicals are also called reactive oxygen species and are singlet oxygen electrons that are highly unstable. To gain stability, they attack healthy cells and acquire electrons from proteins, DNA, or other cellular materials. After losing an electron, these cells become unstable and generate more free radicals, thereby setting up a vicious cycle of cell damage.
This leads to a state known as oxidative stress, which contributes to many disease conditions, including cardiovascular disease, cancers, Alzheimer’s, as well as inflammatory conditions such as chronic venous insufficiency and deep vein thrombosis.
Although the body also produces natural ‘antioxidants’ that neutralize free radicals, in many disease conditions, there can be insufficient production of antioxidants.
In varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency, studies have found lowered antioxidant defense as well as chronic oxidative stress, apart from inflammation that compromises blood flow.
CBD exerts powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties
Researchers have found that CBD controls inflammation by regulating the production of pro-inflammatory substances such as cytokines in immune cells.
According to a 2018 study that was featured in the Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, CBD exerts potent anti-inflammatory effects. Experimental models show CBD influences immune system response with a reduction in cytokine production. Another factor that contributes to inflammatory responses is MCP-2 – or monocyte chemotactic protein-2 that is a type of immune cell (leukocyte). Excessive production of MCP-2 leads to inflammatory responses. Studies show CBD activates cannabinoid receptors (CB2), which reduces MCP-2 production to control inflammation.
Researchers also found in a study that was featured in the British Journal of Pharmacology that CBD has pharmacological potential to reduce acute inflammation. Other studies also support the anti-inflammatory potential of CBD.
Additionally, the antioxidant properties of CBD have been extensively studied. CBD’s antioxidant effect has been shown to be 30 to 50% more than that exhibited by powerful antioxidants such as vitamins C and E.
CBD exerts potent antioxidant effects to neutralize reactive oxygen species that contribute to oxidative stress. Evidence is mounting in support of the fact that this natural compound extracted from Cannabis Sativa can be a viable pharmacological alternative in treating DVT and venous insufficiency.
More articles:



