CBD for Management of Arthritic Pain
Introduction
Regardless of what science says, people suffering with arthritis pain are beginning to turn to CBD for help. Dealing with the chronic pain of arthritis is a daily challenge. Those suffering from arthritis are desperate to find ways to decrease pain and improve sleep and their overall ability to function normally. Most individuals need to take a variety of medications throughout the day and these typically include an opioid-based medication and/or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
As discussed in a previous article, there can be serious side effects from opioid-based medications and NSAIDs. You can read more about these side effects here. Given the potential downside of these medications it is no wonder that more and more people suffering from arthritis are looking for other options. A recent survey conducted by the Arthritis Foundation, discovered that of the more than 2600 patients surveyed, 94% of those who were using CBD were using it for pain management. (1) Although this isn’t a clinical study, there is strong anecdotal evidence to suggest these individuals are receiving the relief they seek.
Facts about Arthritis
Arthritis is a common health problem affecting more than 350 million people globally and it is a leading cause of disability. In fact, among chronic diseases in North America, arthritis causes more disability than any other condition, including heart disease, diabetes, and back or spine problems. (2) Contrary to popular belief, Arthritis is not a disease of the elderly. It affects all ages, races, both genders – but more women than men – and anyone from babies to older people are susceptible.
The disease can be placed into two broad types:
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disease in which a person’s immune system attacks their joints, causing inflammation. RA commonly affects the hands and feet and leads to painful, swollen, and stiff joints.
- Osteoarthritis (OA): A degenerative disease that affects joint cartilage and bones, causing pain and stiffness. It often affects the hip, knee, and thumb joints.
Symptoms
Symptoms of both RA and OA include pain and inflammation around the affected joints and joint stiffness. There is no cure for RA and OA but it is possible to manage the symptoms. Unfortunately, not all patients respond to the same treatments, so Rheumatologists need to work with patients to find the right combination of medications to treat the symptoms.
Treatment
Typical treatments for pain include over-the-counter pain relief such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids and acetaminophen. Unfortunately, opioid-based medications are also being prescribed to manage pain when over-the-counter remedies are ineffective. A disturbing revelation came out of a study conducted by a group of researchers in Canada of 1,204 pre-surgical patients with knee, hip and spine OA to examine the rates of prescription opioid use to manage pain. The results showed that more than 15% of participants reported they sometimes used opioids and 15% reported daily use of opioids. (3)
In a previous article titled “Using Topical CBD Formulations in Sports and Training” the implications of using opioid-based medication and NSAIDs are discussed. Patients using opioids to manage pain are at risk of addiction and overdose while NSAIDs have been linked to increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
In the treatment of RA, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are often prescribed to slow the progression of RA. Newer DMARDs such as Biologics and Janus Kinase inhibitors have varying degrees of effectiveness, however, one of the main problems associated with DMARDs is that they slow down the entire autoimmune system in the body, leaving it open to infections. (4)
Implications of Arthritis on a Global Scale
The Implications of Arthritis in the present and future are concerning. The burden of arthritis worldwide is expected to have significant consequences in terms of health care costs and loss of productivity by patients today, and over the next 30 years. Arthritis doesn’t just cause a person pain; it affects their ability to work and to lead a normal life. Today approximately 1% (77,000,000) of the global population suffers from RA (5) while the 2013 study of the Global Burden of Disease estimated 242 million people worldwide are living with OA. This number is expected to have increased by 2019 due to an aging population.
“The economic burden of arthritis on patients and society is high in every country that it has been estimated. In 2003 the total costs attributable to arthritis and other rheumatic conditions (AORC) in the US was approximately $128 billion equaling 1.2% of the 2003 US gross domestic product. Direct costs totaled $80.8 billion (i.e., medical expenditures) and indirect costs were $47.0 billion (i.e., lost earnings). A US study in 2009 estimated costs due to hospital expenditures of total knee and hip joint replacements to be $28.5 billion and $13.7 billion respectively. When compared to age and gender matched peers, patients with OA have higher out of pocket health-related expenditures with the average direct costs of OA per patient estimated at approximately $2,600 per year. Additionally, job-related indirect costs due to loss of productivity have been estimated to cost from $3.4 to $13.2 billion per year.” (6)
Is CBD the Answer?
The symptoms of Ostio and Rheumatoid arthritis are quite similar; however, OA is a degenerative disease while RA is an autoimmune disease. Treatment of the symptoms is also similar. As noted earlier, treatment is usually a combination of medications to manage pain and fight inflammation. In addition to medications, patients are also encouraged to adopt a low impact exercise regime, get plenty of rest and eat a diet high in Omega 3 fatty acids.
Pre-clinical studies on CBD are promising. In 2006 a study was conducted using an oral spray on 58 human participants with Rheumatoid arthritis. Of the 58 participants, 31 were given an oral spray containing CBD while the other 27 were given placebo. The study concluded that “… a significant analgesic effect was observed and disease activity was significantly suppressed…”. (7) A 2008 review using CBD to treat chronic pain also concluded that CBD reduced pain and improved sleep without any negative side effects. (8) In 2016 another study was done using CBD gel on rats. Researchers again found that the CBD gel reduced both joint pain and inflammation without any side effects. (9)
On top of these studies there are numerous anecdotal reports from people suffering from Ostio and Rheumatoid arthritis, showing that CBD creams and oils are effective in reducing pain and inflammation as well as improving sleep and their overall sense of well-being. (1) Other studies have also suggested the most effective way to administer CBD may be in the form of a topical cream. (10).
In his address at the Annual Meeting of the Congress of Clinical Rheumatology on cannabinoid treatment for rheumatic diseases, Greg Gerdeman, former assistant professor of Biology at Eckerd College in St. Petersburg, Florida had this to say about the use of cannabinoids in the treatment of arthritis: “There’s a lot of legitimate scientific excitement about the use of cannabinoids in rheumatic disease. Doctors should be aware that it’s not going to go away, and they should support a research infrastructure for the best evidence-based medicines in cannabinoids and rheumatic disease.” (11)
The Voice of the Arthritis Foundation
As the leading organization for arthritis, the Arthritis Foundation issued a formal statement to the FDA urging the agency to expedite the study and regulation of CBD products to help make them a safe option for the 54 million people living with arthritis in the USA.
“As the largest organization representing the voice and needs of people with arthritis, the Arthritis Foundation has always welcomed new treatment options because no single drug, supplement or therapy works for everyone. We believe patients should be empowered to find safe management strategies that are appropriate for them. The more options available, the likelier it is that more people will benefit.
We are intrigued by the potential of CBD to help people find pain relief and are on record urging the FDA to expedite the study and regulation of these products. While currently there is limited scientific evidence about CBD’s ability to help ease arthritis symptoms, and no universal quality standards or regulations exist, we have listened to our constituents and consulted with leading experts to develop these general recommendations for adults who are interested in trying CBD.” (12)
The “general recommendations” mentioned in the statement refers to the first “CBD Guidance for Adults with Arthritis”, which was released by the Arthritis Foundation on September24, 2019. (13)
The support for CBD as an alternative treatment for a variety of arthritis symptoms is clearly growing. Several studies have shown that it can be used to address pain and inflammation in joints. The survey conducted by the Arthritis Foundation also found that patients reported improved sleep and overall sense of well being. Not only do we see anecdotal reports from individuals who have turned to it for relief, but the academic world is starting to take notice. The formal statement from the Arthritis Foundation to the FDA is further proof that clinical research will need to be accelerated in the near future.
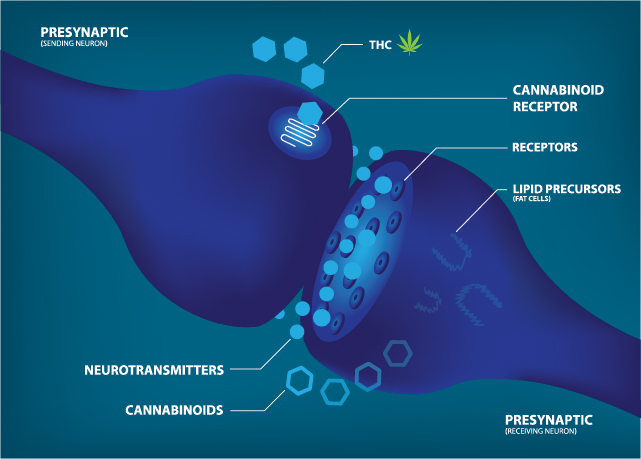
How Does CBD Work?
CBD is a phytocannabinoid that is extracted from both Hemp and Marijuana. In its pure form (CBD isolate) there is no difference between the CBD from either plant. When CBD is ingested or applied topically as a topical formulation such as CBD Pain Relief Cream it begins to interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS consists of three main parts:
1) Endocannabinoids, anandamide (AEA) and arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG) these are cannabinoids produced naturally in your body;
2) CBD receptors referred to asCB1 and CB2 that exist on cells throughout your body;
3) Enzymes, fatty acid amide hydrolase, which breaks down AEA and monoacylglycerol acid lipase, which typically breaks down 2-AG
The ECS works to maintain homeostasis within our body. When we are sick or injured, the appropriate endocannabinoid is released to bind with the CBD receptors and attempt to rebalance the system. Enzymes are also released to break down the endocannabinoid that has bound to one of the CB receptors (for example anandamide binding with CB2 receptors). The process of enzymes breaking down the endocannabinoids is known as “reuptake”.
CBD does not work by binding directly with the receptors the way endocannabinoids and THC do. Instead, it inhibits the reuptake of the endocannabinoid present. In other words – CBD makes the enzyme that should break down the anandamide not work as efficiently as it should. In the case of anandamide, this enzyme is fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). The result is a higher concentration of anandamide in the system thereby increasing its impact.
CBD also inhibits fatty acid-binding protein (FABP).which is responsible for binding to the anandamide already present in the synapse in order to transport it outside the synapse where it is broken down by FAAH. In this case, the CBD competes for the FABP “attention”, taking the place of the anandamide. This causes less anandamide to be metabolized, allowing it to remain in the system longer, again increasing its impact.
CBD for Your Arthritic Pain?
Research and anecdotal evidence seems to indicate that CBD can help as an effective treatment for those suffering from arthritis. As noted above, one group of researchers have mentioned that topical formulations may be more effective than ingesting the CBD because the full dose of CBD will be administered.
If you are thinking of trying CBD, start with a product like Pain Relief CBD Cream from InnoCan Pharma. It leverages the synergistic properties of CBD with known analgesic ingredients like menthol and methyl salicylate. If you find you are not getting the results you should try a stronger formulation such as Extra Strength Pain Relief CBD Cream from InnoCan Pharma.
Conclusion
Individuals suffering from arthritis are turning to CBD as a means of treating their pain and reducing inflammation. They are also reporting that they have better sleep and a greater sense of well-being. Research has shown that CBD holds the promise of being an effective treatment for managing the symptoms of arthritis and it is suspected that this is because of how it affects the uptake of anandamide after it has been produced in the endocannabinoid system. Essentially it prolongs the effect of anandamide in the ECS resulting in reduced inflammation and pain. In the USA there is strong support for CBD from both the Arthritis Foundation and from those conducting research. One can only hope that clinical research will continue to verify what individuals suffering from arthritis are already claiming and the medical community will come together to support and promote the use of CBD in the near future.
Reference Articles
(1) http://blog.arthritis.org/news/patients-tell-us-cbd-use/
(2) https://globalranetwork.org/project/disease-info/
(3) https://www.rheumatology.org/About-Us/Newsroom/Press-Releases/ID/854
(5) https://www.rheumatoidarthritis.org/ra/facts-and-statistics/
(7) https://academic.oup.com/rheumatology/article/45/1/50/1788693
(8) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2503660/
(9) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4851925/
(10) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4151231/
(11) https://www.projectcbd.org/medicine/cannabinoid-treatment-rheumatism-greg-gerdeman-phd
(12) https://www.arthritis.org/about-us/news-and-updates/cbd
(13) https://www.arthritis.org/about-us/news-and-updates/cbd
More articles: