CLX
REVOLUTIONARY CELL THERAPY –
BASED TECHNOLOGY

REVOLUTIONARY CELL THERAPY – BASED TECHNOLOGY, LOADED WITH CBD
CBD DELIVERY BY EXOSOMES PATENT APPLICATION FILED APRIL 6, 2020
Background
Exosomes have emerged as promising nanocarriers for drug delivery and targeted therapy. Exosomes are natural membrane vesicles of endosomal origin, secreted by various cells including mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Exosomes carry proteins, lipids, and genetic materials reflective of their cell origins, which facilitate intercellular communication and induce a multitude of biological effects, locally or distally, such as repairing tissue damage, suppressing inflammatory responses and modulating the immune system. Exosomes are easily traceable and target specific areas.
Recent studies have demonstrated that exosomes derived from MSCs can promote regeneration and improve immune reaction processes in damaged tissues. Exosomes contain anti-inflammatory agents that are able to target inflamed organs.
Research into potential treatments started in January 2020 and several antiviral drugs are in clinical trials[1]. It seems that cell therapy may play a role in treating infection and body immune system reaction. Several clinical studies are conducted using different Stem Cells treatments and Exosomes[2].
All new treatments and drugs under development will need to go through clinical studies to demonstrate safety and effectiveness for the disease.
Exosomes
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are reported to show therapeutic effects in inflammation and injury. Hundreds of clinical studies are using these cells and several endowments have already been approved for use by the Food and Drug Administration in the US (FDA). In the recent years, studies have reported that MSC-derived nano patrticals, named “exosomes”, have functions similar to those of MSCs, such as repairing tissue damage, suppressing inflammatory responses and modulating the immune system.
Exosomes are endosome-derived small membrane vesicles, approximately 30 to 100 nm in diameter, and are released into extracellular fluids by cells in all living systems. They are generated by many cell types and contain proteins and lipids but also mRNAs and microRNAs (miRNAs)[3]. Exosomes are well suited for small functional molecule delivery. Increasing evidence indicates that exosomes have a pivotal role in cell-to-cell communication[4]. In contrast to transplanted exogenous MSCs, the MSC-derived exosomes do not proliferate, are less immunogenic, and are easier to store and deliver than MSCs.
Recently, it has been shown that the secretion of different factors through exosomes, orchestrate the principle mechanisms of action of MSCs after infusion. The use of MSC-derived exosomes may provide considerable advantages over their counterpart live cells, potentially reducing undesirable side effects including infusional toxicities (Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for clinical use[5]. Exosomes can be loaded with different molecules. Exosomes can carry and deliver molecules to damaged areas and may have therapeutic effect[6].
In contrast to transplanted MSCs, the MSC-derived exosomes do not proliferate, are less immunogenic and are easier to store and deliver than MSCs[7]. Exosomes have been characterized, their content was identified and studies from Prof. Offen’s laboratory at Tel Aviv University, Israel, demonstrated that they can migrate and concentrate inside inflamatory lesions and recover damaged tissues[8],[9] (see top picture below).
Many studies showed that exosomes can efficiently deliver cargo, such as drugs, to the target cell. Therefore, exosomes can be used to deliver therapeutic cargo for treatment[10].
Recently, research teams led by Prof. Shulamit Levenberg of the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel and Prof. Offen used loaded exosomes in rats after spinal cord leasion. They demonstrated that intranasal delivery of the loaded exosomes significantly elicited functional recovery in the rats with complete spinal cord injury[11].
The capacity of exosomes to provide protection to injured tissue after stroke and respiratory distress syndrome was the subject of a recent study[12],[13]. In addition, the use of exosomes in the treatment of severe coronavirus pneumonia is also the subject of a recent study[16].
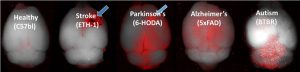
Exosomes migrate damaged areas in the brain

Brain imaging by gold nano articles
Cannabidiol (CBD)
For several years, CBD derived from the cannabis plant has been the subject of research and medicine because of its value and its safety profile in humans. Studies have demonstrated that CBD exerts a number of beneficial pharmacological effects.
InnoCan’s unique, breakthrough approach is based on the following three (3) elements:
1.Exosomes demonstrated benefits in many medical conditions, including the “homing” to lesions. The fact that exosomes are a thousand times smaller than cells, may allow them to easily approach endothelial infected cells and reduce the diffuse endothelial inflammation.
2. The CBD safety profile is known and it is being used in several different clinical studies.
3. Prof Offen has developed novel technology to load exosomes with different molecules. InnoCan in conjaction of Tel Aviv Univercity are developing a platform to allow the loading of CBD to the exosome and expects to obtain synergetic effects. The development will involve several milestones, such as loading the chosen cannabinoids such as CBD to MSC-Exosomes and proof of concept in animal models of various diseases.
[1] https://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-health-hospital-idUSKBN20B1M6
[2]https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/news/116794/us-researchers-to-study-stem-cell-therapy-in-covid-19-patients/
[3] https://thejns.org/view/journals/j-neurosurg/122/4/article-p856.xml#b70-jns14770
[4] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006295211009531
[5] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41409-019-0616-z
[6] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31454225
[7] Phinney DG, Pittenger MF. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells. 2017 Apr;35(4):851-858.
[8] Perets N, Betzer O, Shapira R, Brenstein S, Angel A, Sadan T, Ashery U, Popovtzer R, Offen D. Golden Exosomes Selectively Target Brain Pathologies in Neurodegenerative and Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Nano Lett. 2019 Jun 12;19(6):3422-3431.
[9] Betzer O, Perets N, Angel A, Motiei M, Sadan T, Yadid G, Offen D, Popovtzer R. In Vivo Neuroimaging of Exosomes Using Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2017 Nov 28;11(11):10883-10893.
[10] Yeo RW, Lai RC, Zhang B, Tan SS, Yin Y, Teh BJ, Lim SK. Mesenchymal stem cell: an efficient mass producer of exosomes for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2013 Mar;65(3):336-41.
[11] Guo S, Perets N, Betzer O, Ben-Shaul S, Sheinin A, Michaelevski I, Popovtzer R, Offen D, Levenberg S. Intranasal Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Loaded with Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog siRNA Repairs Complete Spinal Cord Injury. ACS Nano. 2019 Sep 24;13(9):10015-10028.
[12] Otero-Ortega L, Laso-García F, Gómez-de Frutos M, Fuentes B, Diekhorst L, Díez-Tejedor E, Gutiérrez-Fernández M. Role of Exosomes as a Treatment and Potential Biomarker for Stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 2019 Jun;10(3):241-249.
[13] Horie S, Gonzalez HE, Laffey JG, Masterson CH. Cell therapy in acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Thorac Dis. 2018 Sep24] Atalay S, Jarocka-Karpowicz I, Skrzydlewska E. Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Cannabidiol. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Dec 25;9(1)
[14] Vuolo F, Abreu SC, Michels M, Xisto DG, Blanco NG, Hallak JE, Zuardi AW, Crippa JA, Reis C, Bahl M, Pizzichinni E, Maurici R, Pizzichinni MMM, Rocco PRM, Dal-Pizzol F. Cannabidiol reduces airway inflammation and fibrosis in experimental allergic asthma. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 15;843:251-259
[14] Jadoon KA, Tan GD, O’Sullivan SE. A single dose of cannabidiol reduces blood pressure in healthy volunteers in a randomized crossover study. JCI Insight. 2017 Jun 15;2(12)
[16] https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)30937-5/fulltext

